Related Resources: material science
Rankine Gordon Equation
Rankine Gordon Equation
Predictions of buckling loads by the Euler formula is only reasonable for very long and slender struts that have very small geometrical imperfections. In practice, however, most column struts suffer plastic knockdown and the experimentally obtained buckling loads are much less than the Euler predictions. For struts in this category, a suitable formula is the Rankine Gordon equation which is a semi-empirical formula, and takes into account the crushing strength of the material, its Young's modulus and its slenderness ratio.
A comparison of the Rankine-Gordon and Euler equation, for geometrically perfect struts, is given below:
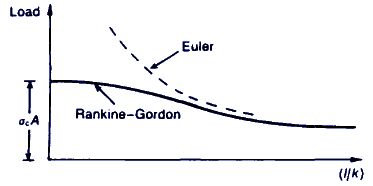
Comparison of Euler and Rankine-Gordon equation
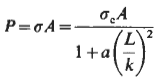
![]()
Where:
σ = failure stress
σc = elastic limit in compression
a = constant
A = cross-sectional area
k = least radius of gyration
L = Length
P = Buckling Load
I = Area moment of Inertia
|
Material
|
σc |
a
|
|
|
Pinned Ends
|
Fixed Ends
|
||
|
Mild Steel |
320
|
1/7500
|
1/30000
|
|
Wrough Steel
|
250
|
1/9000
|
1/36000
|
|
Cast Iron
|
550
|
1/1600
|
1/6400
|
|
Wood
|
35
|
1/3000
|
1/12000
|