Related Resources: fluid flow
Pex (Cross-Linked Polyethylene) Specifications
Fluid Flow Table of Contents
Hydraulic and Pneumatic Knowledge
Pex (Cross-Linked Polyethylene) Specifications, design use and installation and sizes.
Pex (Cross-Linked Polyethylene): PEX was first used for hot-water radiant heating in the early 1970's, and today is a reliable solution around the world for hot- and cold water plumbing, radiant heating and cooling, outdoor snow and ice melting, residential fire protection, hydronic (hot-water) building services piping, and other demanding applications such as natural gas piping (outside of North America).
PEX is a polymeric material formed by the chemical joining of individual polyethylene molecules in a process called cross-linking. Cross-linking alters the performance of the original polyethylene polymer improving several key properties. The primary reason for cross-linking polyethylene (PE) is to increase the material's elevated temperature performance under load. In addition, cross-linking substantially improves the pipe's environmental stress crack resistance (ESCR), resistance to slow crack growth, chemical resistance, toughness and abrasion resistance.
 |
|---|
Uses of Cross-Linked Polyethylene (PEX) Tubing
- Residential and commercial potable cold- and hot-water distribution systems
- Residential fire protection systems
- Hydronic radiant heating and cooling, using warm or chilled fluids
- Outdoor snow and ice melting
- Outdoor turf conditioning
- Ice surface piping
- Hot-water distribution piping
- Hot-water baseboard piping
- Warm- and hot-water radiator connection piping
- Potable water service pipes
- Geothermal ground loop heat exchangers
- Chilled water piping
- Specialized industrial and mining applications PEX is typically not used for refrigerant line piping or medical gas applications
- Pex tubing is available in a variety of colors
Standard Pex Size Dimensions:
|
Nominal
PEX Size inch |
Outside
Diameter inch |
Inside
Diameter inch |
Wall
Thickness, inch |
|---|---|---|---|
|
3/8
|
0.500
|
0.350
|
0.070
|
|
1/2
|
0.625
|
0.475
|
0.070
|
|
5/8
|
0.750
|
0.574
|
0.083
|
|
3/4
|
0.875
|
0.677
|
0.097
|
|
1
|
1.125
|
0.863
|
0.125
|
Bend Radius Design PEX
|
PEX Size
inch |
Outside
Diameter inch |
Minimum
Inside Bend Radius inch |
|---|---|---|
|
3/8
|
0.500
|
4
|
|
1/2
|
0.625
|
5
|
|
5/8
|
0.750
|
6
|
|
3/4
|
0.875
|
7
|
|
1
|
1.125
|
9
|
Fluid Performance PEX (Approximate)
|
PEX Size
inch |
Volume
Gal/100 ft |
Weight
lbs / 100 ft |
|---|---|---|
|
3/8
|
0.500
|
4.50
|
|
1/2
|
0.920
|
5.80
|
|
5/8
|
1.340
|
8.38
|
|
3/4
|
1.830
|
11.00
|
|
1
|
3.030
|
17.06
|
PEX Pressure Drop Table (psi per 100ft of tubing length)
|
Flow Rate
GPM |
Pex Tubing Size
|
||||
|
3/8"
|
1/2"
|
5/8"
|
3/4"
|
1"
|
|
|
0.5
|
2.50
|
0.51
|
0.21
|
0.05
|
0.02
|
|
1.0
|
7.50
|
1.70
|
0.71
|
0.34
|
0.10
|
|
2.0
|
26.1
|
5.30
|
2.12
|
1.02
|
0.35
|
|
3.0
|
54.1
|
11.0
|
4.36
|
2.10
|
0.63
|
|
4.0
|
-
|
18.4
|
7.36
|
3.53
|
1.06
|
|
5.0
|
-
|
27.4
|
11.0
|
5.26
|
1.58
|
|
6.0
|
-
|
38.1
|
15.3
|
7.30
|
2.19
|
|
7.0
|
-
|
-
|
20.1
|
9.63
|
2.89
|
|
8.0
|
-
|
-
|
25.6
|
12.3
|
3.68
|
|
9.0
|
-
|
-
|
31.7
|
15.1
|
4.55
|
|
10.0
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
18.3
|
5.50
|
|
11.0
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
21.7
|
6.52
|
|
12.0
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
25.4
|
7.63
|
|
13.0
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
8.81
|
|
14.0
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
10.1
|
|
15.0
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
11.4
|
1 psi = 2.3 ft of head (for fresh water), or 1 ft of head = 0.434 psi
Pressure Ratings: Pressure rating of plastic pipe is highly dependent on material, as well as wall thickness. Most commercially available plastic pipe will be rated by the manufacturer.
PEX pressure ratings are 160 psi at 74°F and 100 psi at 180°F.
Elongation (linear expansion): Typical elongation is anywhere from 1" to 2.5" for every 100ft of PEX pipe at a 10°F temperature rise. Since PEX expands and contracts with temperature changes, it should be secured so as to provide sufficient space for expansion to occur.
PEX pipe is typically connected using either a copper crimp ring or expansion fittings with outer expansion rings. In the crimping method, a copper crimp ring is put over the pipe near the end, a copper fitting is inserted into the pipe end, and a crimping tool is used to crimp the ring over the pipe and fitting. In the expansion fitting method, an expansion tool is used to open the diameter of the pipe, into which an expansion fitting is inserted.
Specifications and Standards
ASTM F876: Standard Specification for Crosslinked Polyethylene (PEX) Tubing.
ASTM F877: Standard Specification for Crosslinked Polyethylene (PEX) Plastic Hot and Cold Water Distribution Systems.
ASTM F1807 – Standard Specification for Metal Insert Fittings Utilizing a Copper Crimp Ring for SDR 9 Cross-linked Polyethylene (PEX) Tubing and SDR 9 Polyethylene of Raised Temperature (PE-RT) Tubing
ASTM F1960 – Standard Specification for Cold Expansion Fittings with PEX Reinforcing Rings for use with Cross-linked Polyethylene (PEX) Tubing
ASTM F2159 – Standard Specification for Plastic Insert Fittings Utilizing a Copper Crimp Ring for SDR9 Cross-linked Polyethylene (PEX) Tubing and SDR 9 Polyethylene of Raised Temperature (PE-RT) Tubing
ASTM F2080 – Standard Specification for Cold-Expansion Fittings With Metal Compression-Sleeves for Cross-Linked Polyethylene (PEX) Pipe
ASTM F2098 – Standard Specification for Stainless Steel Clamps for Securing SDR9 Cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) Tubing to Metal Insert Insert and Plastic Insert Fittings
CSA B137.5 – Cross-linked Polyethylene (PEX) Tubing Systems for Pressure Applications
ANSI/AWWA C904-06 – AWWA Standard for Cross-Linked Polyethylene (PEX) Pressure Pipes 1/2 inch (12 mm) through 3 inch (76 mm) for Water Service
ASTM F2023: Oxidative resistance of PEX to Hot Chlorinated Water per NSF protocol P171 (Non-Barrier PEX Tubing).
CSA B137.5: Crosslinked Polyethylene (PEX) Tubing Systems for Pressure Applications.
NSF/ANSI 14, nsf-rfh: Evaluated for use in Radiant Floor Heating (NSF-rfh) Applications (Oxygen Barrier PEX tubing).
NSF/ANSI 61-G, NSF/ANSI 372, nsf-pw-g: Complies with NSF/ANSI standard 61-G for Lead-Free Drinking Water System Components (Non-Barrier PEX Tubing).
UPC listed by IAPMO (International Association of Plumbing and Mechanical Officials).
Specification example:
ASTM F876 “Standard Specification for Crosslinked Polyethylene Tubing”
- Pipes are CTS, SDR9, with tight tolerances on dimensions
- Minimum Quick Burst Capability:
- 475 psi @ 73.4°F, 210 psi @ 180°F, 180 psi @ 200°F
- Long-term Pressure Ratings:
- 160 psi @ 73.4°F, 100 psi @ 180°F, 80 psi @ 200°F
- Sustained Pressure Tests
- Up to 16,000 hours accelerated laboratory hydrostatic testing is required for PPI “Standard Grade” listings
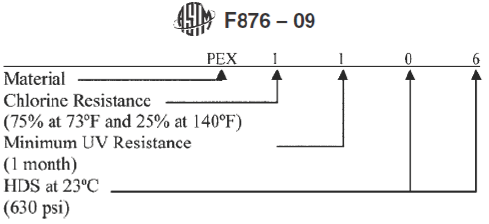
- ASTM F876 has categories for performance in three key properties*
*PEX pipes have no “cell classification” • - Performance categories are defined in the “Material Designation Code”
- Example shown from ASTM F876
Related:
- National Standard Taper Pipe Threads NPT Chart
- Fluid Flow Engineering and Design Resources
- Hydraulic, Pneumatic Engineering & Design
- Schedule 40 Steel Pipe Sizes & Dimensions ANSI
- Schedule 80 Steel Pipe Sizes & Dimensions ANSI
- Standard Size Steel Pipe Weights With Contents Calculator
- Extra Strong (XS) Size Steel Pipe Weights Calculator
- Double Extra Strong (XXS) Size Steel Pipe Weights Calculator
- Velocity and Flow Capacity of Oil Standard Tubes
- Velocity and Flow Capacity of Oil Schedule 40 Pipe
- Velocity and Flow Capacity of Oil Schedule 80 Pipe
- Velocity and Flow Capacity of Oil Schedule 160 Pipe