Related Resources: fluid flow
Capillary Action Review and Equations
Capillary Action is due to both the cohesive forces between liquid molecules and adhesive forces of liquid molecules. It shows up as the difference in liquid surface elevations between the inside and outside of a small tube that has one end submerged in the liquid (Fig. 1).
Capillarity is commonly expressed as the height of this rise. In equation form,
h = ( 2 · σ · cosθ ) / [ ( w1 - w2 ) r ]
Where:
h = capillary rise, ft (m),
σ = surface tension, lb/ft (N/m),
w1 and w2 = specific weights of fluids below and above meniscus, respectively, ft (m),
θ = angle of contact,
r = radius of capillary tube, ft (m)
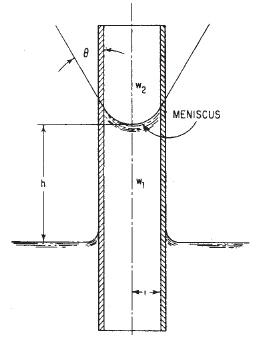
Figure 1
Capillary action raises water in a small-diameter tube. Meniscus, or liquid surface, is concave upward.
Reference:
Civil Engineering Formulas SEcond Edition, Tyler G. Hicks, P.E.
Related:
- Capillary Number and Pressure Formulas and Calculators
- Viscometer Design and Application Review
- Orifice Plate Flow Calculations and Design
- Orifice Plate Type Flow Detector Review
- Orifice Plate Flow Calculation Python Application per. ISO 5167
- Nozzle Venturi and Orifice Flowmeter Formula and Calculator
- Extended Bernoulli Concepts and Equations
- Simplified Bernoulli Equation - Fluid Flow Hydraulic and Pneumatic
- Straight Labyrinth Seal Flow Equation and Calculator
- Manometer Application Equation for Pressure Manometer is an instrument for measuring gas or vapor pressure- especially at low levels.
- Manometer Pressure Calculator U-Tube Manometer Measuring Pressure Calculator