Related Resources: heat transfer
Parallel Plates Channel Natural Convection Equation and Calculator
Heat Transfer Engineering
Thermodynamics
Engineering Physics
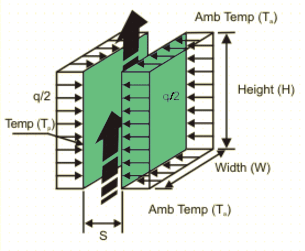
Vertical Parallel Plates Channel Natural Convection Equation and Calculator
Average heat transfer coefficient and surface temperature for an isoflux (constant and uniform flux) parallel plate vertical channel open to ambient from both ends in a natural convection environment. The convection calculation are based on Rayleigh number.
ALL calculators require a Premium Membership
Preview: Vertical Parallel Plates Channel Natural Convection Calculator
Fluid Properties at Film Temperature (Default is for Air at 20C)
Calculations is based on Nusselt number correlations.
Tp = Ta + q / H A
h = Nu · k / S
The Nusselt number is calculated as:
Nu = { 48 / (Ras · S/L) + 2.51 (Ras· S/L)(2/5) }-0.5
where:
Ras = g Bq ρ2 Cp S4 / k2 μ
Ras (S/L) <= 10 corresponds to the fully developed case and
Ras (S/L) >= 100 correspond to the isolated plate limit, i.e. for short channel or large spacing independent boundary layers develop on each plate, and the conditions are those of an isolated plate in a quiescent medium.
Prandt Number:
Pr = Cp · μ / k
Rayleigh Number:
Ra = g · B · q ' · S4 · ρ2 * Cp / (μ· k2 )
Film temperature at the reference temperature of 20 °C.
Tf = (Tp + Ta ) / 2
Fluid density at at film temperature using perfect gas law:
ρ = ρref ( Tref + 273) / ( Tf + 273) + 273
Tref = 20 °C
Where:
Tf = Film temperature °C
Tp = Plate temperature °C
Ta = Ambient Temperature °C
Cp = Specific Heat J/kg- °C
B = Coefficient of thermal expansion (1/K)
k = Thermal Conductivity (W/m - °C)
v = Dynamic Viscosity ( kg/m-s )
ρ = Density (kg/m3)
Nu = Nusselt Number
W = Width of Channel (m)
H = Height of Channel (m)
S = Channel Gap (m)
q = Total uniform heat load on plates (W)
q' = Flux Heat (W/m2)
Pr = Prandtl number
Ra = Raleigh number - for a fluid is a dimensionless number associated with buoyancy-driven flow, also known as free convection or natural convection.
h = Average heat transfer coefficient (W/m2 - °C)
g = 9.81 (m/s2)
References
Bar-Cohen, A., and W.M. Rohsenow, AThermally Optimum Spacing of Vertical Natural Convection Cooled, Parallel Plates, J. Heat Transfer, 106, 116 1984.
Incropera, De Witt., Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer , 3rd ed., John Wiley & Sons, p557, eq.9.46, 1990.