Related Resources: fluid flow
Aerodynamics Airfoil Theory Equations
Aerodynamics Airfoil Theory Equations
Open: Airfoil Lift and Characteristics Calculator
The lift force on an airfoil is given by
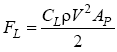
CL = the lift coefficient
ρ = fluid density
V = velocity (m/s) of the undisturbed fluid and
Ap = the projected area of the airfoil as seen from above (plan area). This same area is used in defining the drag coefficient for an airfoil.
The lift coefficient is accurately determined by test experimentally. The lift coefficient can be approximated by the equation:
CL = 2 π k1 sin ( α + β ) which is valid for small values of α and β
alternatvely
CL = 2 L / ( A ρ V2 )
k1 = a constant of proportionality
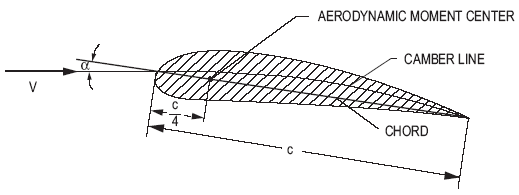
α = angle of attack (angle between chord of airfoil and direction of flow)
β = negative of angle of attack for zero lift.
The drag coefficient may be approximated by:
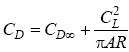
CD∞ = infinite span drag coefficient
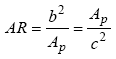
The aerodynamic moment is given by:
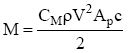
where the moment is taken about the front quarter point of the airfoil.
MC = moment coefficient
Ap = plan area
c = chord length
Reference:
Fundamentals of Engineering, seventh Edition National Council of Examiners for Engineering amd Surveying
Related:
- Aircraft Aeroelasticity and Loads Introduction
- Aeronautical Engineering and Airplane Design
- Aerodynamic Drag Equation and Calculator
- Aerodynamics of Wind Turbines
- Aerodynamic Noise in Control Valves Mass Spreadsheet Calculator
- Aerodynamic Noise Volumetric Control Valves Mass Spreadsheet Calculator
- Helicopter Engineering Design Handbook Part One
- Wind Turbine Blade Design
- Wind Power Generation and Wind Power Turbine Design
- Aircraft Airframe Handbook Mechanics
- Airfoil AeroDynamics Characteristics Calculator
- Aviation Maintenance Technician Handbook Powerplant (FAA-H-8083-32A) Volume 2
- Aviation Maintenance (FAA-H-8083-30A) Technician Handbook General