Related Resources: Engineering Conversions Equivalent
Electric and Magnetic Quantities Units and Conversions
Engineering Conversions and Equivalents
Electric and Magnetic Quantities Units and Conversions
Where:
Length = L
Mass = M
Time = T
Current = Q/T
Charge = Q
Electric and Magnetic Quantities
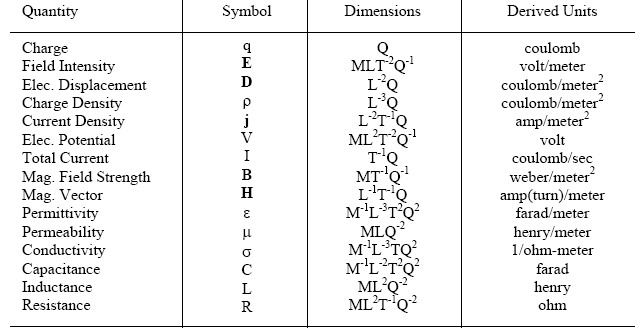
Conversion of mksq Units to Gaussian Units
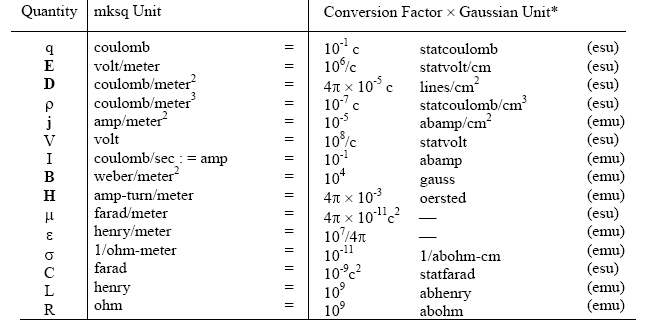
*c = vel. of light (free space) in cm/sec ≈ 3 × 1010 Use of table:
1 coulomb = 10-1 (3 × 1010) statcoulomb = 3 × 109 statcoulomb
|
QUANTITY
|
SYMBOL
|
SI UNIT
|
SI
EQUATION |
CGS
UNIT |
CGS
EQUATION |
CONVERSION
FACTOR |
|
Magnetic
induction |
B
|
tesla (T)
|
B=µ o (H+M)
|
gauss (G)
|
B = H+4πM
|
1 T = 10 4 G
|
|
Magnetic
field strength |
H
|
ampere/ meter
(A/m) |
H = N×I/lc
( lc - magnetic path, m) |
oersted (Oe)
|
H = 0.4πN×I/lc
(lc - magnetic path, cm) |
1 A/m =
4π×10 -3 Oe |
|
Magnetic flux
|
Φ
|
weber (Wb)
|
Φ = B×Ac
(Ac - area, m 2 ) |
maxwell (M)
|
Φ = B×Ac
(Ac- area, cm 2 ) |
1 Wb = 10 8 M
|
|
Magnetization
|
M
|
ampere/ meter (A/m)
|
M=m/V
(m- total magnetic moment, V- volume, m 3 ) |
emu/cm 3
|
M=m/V
(m- total magnetic moment, V- volume, cm 3 ) |
1 A/m = 10 -3
emu / cm 3 |
|
Magnetic
permeability of vacuum |
µ o
|
newton/ ampere 2
|
µ o = 4π×10 -7
|
1
|
-
|
4π×10 -7
|
|
Inductance
|
L
|
henry
|
L=μ o μN 2 Ac/lc
(Ac- area, m 2 , lc - magnetic path, m) |
henry
|
L=0.4πμN 2 Ac/lc×10 -8
(Ac-area, cm 2 , lc - magnetic path, cm) |
1
|
|
Emf (voltage)
|
V
|
volt
|
V=-N×dΦ/dt
|
volt
|
V= - 10 -8 N×dΦ/dt
|
1
|
|
Note: in the above equations: N- turns, I - current (in amps)
|
||||||